The issue of animal cruelty in factory farms is a significant concern in today's food production landscape. Factory farms, also known as industrial farms, prioritize efficiency and profitability, often at the expense of animal welfare. Understanding the realities of animal cruelty in factory farms is crucial for making informed choices about the food we consume and advocating for more humane farming practices.
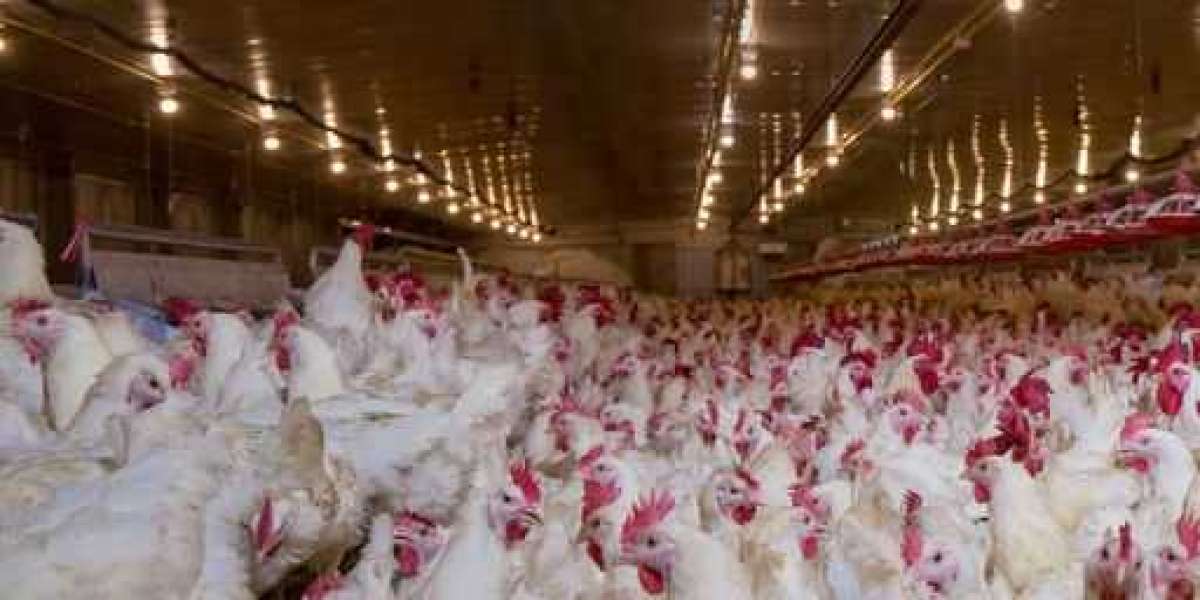
Animal cruelty in factory farms manifests in several distressing ways. The conditions in which animals are kept are frequently deplorable. Factory farms are designed to maximize output and minimize costs, leading to overcrowded, unsanitary environments where animals have little room to move or exhibit natural behaviors. For example, chickens are often confined to cramped cages, pigs are housed in restrictive gestation crates, and cows are kept in tight quarters, which can lead to significant physical and psychological stress.
One of the most egregious forms of animal cruelty in factory farms involves routine mutilations without anesthesia. Animals may undergo procedures such as tail docking, beak trimming, and dehorning, all performed to prevent them from injuring each other or to facilitate their confinement. These procedures cause considerable pain and distress, highlighting the ethical concerns associated with industrial farming practices.
The health issues resulting from animal cruelty in factory farms are also alarming. The stressful conditions and lack of proper veterinary care often lead to diseases and injuries among farm animals. For instance, overcrowding can result in the rapid spread of infections, while poor living conditions can lead to chronic lameness and respiratory problems. In many cases, animals suffering from these conditions are not given adequate medical treatment, exacerbating their suffering and compromising their well-being.
Addressing the issue of animal cruelty in factory farms requires a multifaceted approach. Increased awareness and consumer advocacy are essential for driving change. By choosing to support farms that adhere to higher animal welfare standards, such as free-range or pasture-based operations, consumers can help reduce the demand for factory-farmed products. Additionally, supporting legislative efforts that promote stricter animal welfare regulations can contribute to improving conditions on factory farms.
Education and advocacy play critical roles in addressing animal cruelty in factory farms. Organizations dedicated to animal welfare work tirelessly to expose the harsh realities of factory farming and promote more humane alternatives. These efforts include documenting conditions on factory farms, campaigning for legislative changes, and educating the public about the ethical implications of their food choices.
In conclusion, animal cruelty in factory farms is a pressing issue that reflects the broader ethical challenges of modern food production. The inhumane conditions, routine mutilations, and health issues faced by animals in factory farms highlight the urgent need for reform. By raising awareness, supporting humane farming practices, and advocating for stronger animal welfare regulations, individuals can contribute to creating a more ethical and compassionate food system. Understanding the impact of factory farming on animal welfare is crucial for making informed choices and driving meaningful change in how we produce and consume food.